We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +1 7204454674 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

ISO 27001 is the internationally recognised standard published jointly by ISO and IEC in 2005. ISO 27001 was further revised in 2013 to tackle security risks. A new European version of ISO/IEC 27001 was updated and published in 2017 after making two revisions in Clause 6.1.3 and Annex A Control 8.1.
In 2020, a large-scale study was conducted to address the effectiveness of ISO/IEC 27001 Certification. While these additions and amendments have been made over the years, a lot of people still don’t know what ISO 27001 Controls really do. The purpose of establishing ISO 27001 is to deal with how to manage information security in specific situations.
ISO 27001 covers all types of domains of an organisation, technology, and people through a list of security Controls that are carefully selected. The following blog will guide you through the intricacies surrounding the ISO 27001 Controls. Stay tuned till the end!
Table of Contents
1) What is ISO 27001 Annex A?
2) Is there a difference between ISO 27001 and ISO 27002
3) How many ISO 27001 Controls are present?
4) The 14 categories of ISO 2001 Controls
5) Who is responsible for implementing Annex A Controls?
6) Is it necessary to adopt ISO 27001 in an organisation?
7) Conclusion
What is ISO 27001 Annex A?
ISO 27001 is one of the best International Information Security Standards set for ISMS (Information Security Management Systems) and their requirements. The controls enlisted in the Annex are used to ensure asset information security. The standard controls of ISO 27001 are defined/outlined in ISO 27001 Annex A.
Based on the scope of your organisation, you are at leverage to select from 114 measures specified in ISO 27001 Annex A – a portfolio for information security controls.
Is there a difference between the ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 Standards?
The ISO 27001 Annexure does not go in-depth with each Control in the Standard. Rather, every Control has been explained in a line or two, which gives the reader a very brief idea of what they have to accomplish. It however does not explain how they can execute it.
The lack of executable information is the reason why the ISO 27002 Standard was created. Its format is the same as the ISO 27001 Annexure, where it encompasses all the Controls from 27001. It however contains a much more extensive description on how the Controls can be put to practice.
Organisations must note that it is helpful for them to follow both ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 Standards, so that they are able to manage their Information Security even better, The ISO 27002 comprises over 90 Controls and the ISO 27001 comprises over 100 Controls.
Furthermore, the ISO 27001 Checklist does not go into too much detail as the ISO 27002 does, because it would become complicated and very lengthy. It instead provides organisations with a meticulous outline of every aspect of an Information Security Management System or ISMS. It also contains advice specific to additional standards.
Moreover, the ISO 27001 is a Standard that encompasses a complete list of compliance requirements for organisations. On the contrary, the ISO 27002 only addresses one aspect of an ISMS.
More importantly, organisations must note that not all the Controls in Information Security will be applied to them while they implement an ISMS. ISO 27001 makes it very clear to organisations that they need to conduct a mandatory Risk Assessment procedure.
This procedure ensures the identification and prioritisation of threats to their ISMS. On the contrary, the ISO 27002 Standard does not explicitly make this clear. This owes to the reason why organisations will find it nearly impossible to identify the Information Security Controls they need to adopt if they choose to apply the ISO 27002 Standard.
Organisations must thoroughly go through each Standard before finalising their decision to stick to one, as each is constituted with very distinct objectives and is only helpful in different circumstances.
If an organisation is just starting off with a new standard or is planning to implement their ISMS framework, the ISO 27001 Latest Version will be best suited to their requirements. If an organisation has successfully identified the Information Security Controls that are necessary to implement, the ISO 27001 Requirements will be suited. to help them learn more about how each Control works.
How many ISO 27001 Controls are Present?
The Controls in Annex A of 27001 are divided into 14 categories. For effective Risk Management, these 14 categories have 114 ISO 27001 Controls outlined as tools. The controls can be applied based on the results of the Risk Assessment of your organisation.
The objective of this framework is to safeguard the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information.
To understand which areas of organisation the Control sets are related to, check the following list of Annex A controls breakdown.
|
Focus Area |
Total Controls |
Category list for Annex A Control |
|
Organisational Issues |
24 |
A.5 A.6 A.8 A.15 |
|
Human Resource |
6 |
A.9 A.10 A.12 A.13 A.14 A.16 A.17 |
|
Information Technology (IT) |
61 |
A.9 A.10 A.12 A.13 A.14 A.16 A.17 |
|
Physical Security |
15 |
A.11 |
|
Legal issues |
8 |
A.18 |
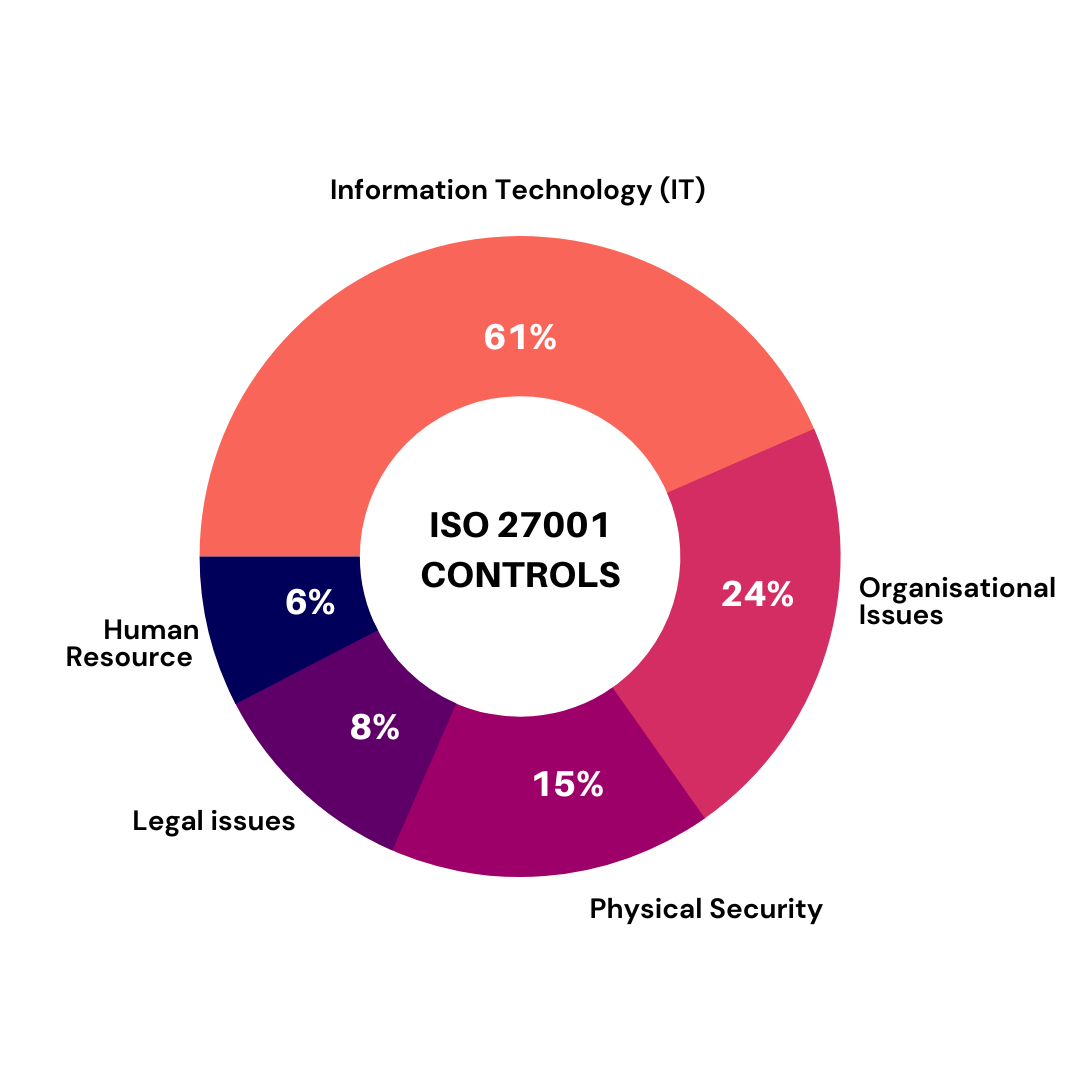
The 14 Categories of ISO 27001 Controls
The 14 Control Categories of ISO 27001 Annex A can be listed down as follows:
1) Information Security policies
2) Organisation of Information Security
3) Human Resources Security
4) Asset Management
5) Access Control
6) Cryptography
7) Physical and environmental security
8) Operational Security
9) Communications Security
10) Systems acquisition, development and maintenance
11) Supplier relationships
12) Information Security incident management
13) Information Security aspects of business continuity management
14) Compliance
Each of the 14 categories of Annex A Controls have specific objectives and security areas to improve Information Security. A total of 114 Controls are grouped under the 14 categories of ISO 27001 Annex A.
Below is the Comprehensive list of the 14 Control Categories:
1) Annex A.5 - Information Security policies (2 Controls)
Objective:
To keep control over the policies related to Information Security and ensure they are written and reviewed according to the organisational requirements.
2) Annex A.6 - Organisation of Information Security (7 Controls)
Objective:
To manage the framework and assign the roles and responsibilities to be implemented in Information Security.
To establish security guidelines on employees' access, information storage, and processing.
3) Annex A.7 - Human Resource Security (6 Controls)
Objective:
To brief the allied parties of the organisation to understand the terms and conditions, responsibilities, and other requirements necessary during the employment tenure.
This category also involves conducting background verification, executing formal disciplinary processes, and adhering to Information Security policies to protect the interests of the organisation.
4) Annex A.8 - Asset management (10 Controls)
Objective:
To classify, identify, manage, and prevent information of assets from being exposed.
It also helps implement classification schemes, define what can be used, and outline procedures to implement and safely dispose of information and media.
5) Annex A.9 - Access Control (14 Controls)
Objective:
Preventing unauthorised access to protect critical information (like PINs and Passwords).
To limit and implement Access Control policy and rights and regulate programs with override capabilities.
6) Annex A.10 - Cryptography (2 Controls)
Objective:
Maintain the authenticity and confidentiality of vital information to ensure key management and encryption.
Also, it outlines Cryptographic policies, keys, usability, and validity period.
7) Annex A.11 - Physical and environmental security (15 Controls)
Objective:
To prevent and have control over interruptions caused during operations due to unauthorised access. Also, to prevent theft, loss, or damage of assets.
It also includes provisions for securing transport bays, regular equipment services and maintenance, defining and implementing a physical security perimeter against potential threats.
8) Annex A.12 - Operational security (14 controls)
Objective:
To protect facilities from malware, maintain consistency across activity logs, avoid loss of data, reduce disruptions, and mitigate technical risks ensuring the integrity of information processing facilities.
This involves creating awareness among users, installing anti-malware software, following backup policies, evaluating risks regularly, documenting the procedures, and monitoring software installations.
9) Annex A.13 - Communications security (7 Controls)
Objective:
To monitor internal and external information transfer.
Implement network security and information transfer policies across the organisations’ communication facilities.
10) Annex A.14 - System acquisition, development and maintenance (13 Controls)
Objective:
When installing new systems or updating existing systems ensure those Information Security requirements are met across the information system.
Ensure that only authorised personnel have the access to the data used for testing.
Regulate testing security facilities, establish secure development areas, and avoid misrouting through public networks, and unauthorised disclosures.
11) Annex A.15 - Supplier Relationships (5 Controls)
Objective:
Maintain an agreed level of information security with your suppliers and ensure that access to valuable information and assets is protected.
This involves formal risk mitigation agreements requiring regulatory approvals, audits, and ongoing monitoring. The ISO 27001 Audit process ensures systematic reviews, verifying compliance with information security standards and enhancing overall risk management.
12) Annex A.16 - Information Security incident management (7 Controls)
Objective:
Includes effective and consistent management of information security incidents.
Involves rapid incident response in line with established procedures through appropriate management channels.
13) Annex A.17 - Information Security aspects of business continuity management (4 Controls)
Objective:
To ensure that the information processing facilities are available to confirm the organisations’ continuity plans of Information Security.
14) Annex A.18 - Compliance (8 Controls)
Objective:
Ensure the organisational requirements are met to carry out Information Security to avoid security risks/breaches of a statutory, legal, and contractual nature.
ISO 27001 Compliance involves safeguarding against any implications such as loss or theft to ensure the protection of sensitive information, review and identify the compliance requirements of the information system.
Plan and conduct your Internal Audits by signing up for our ISO 27001 Internal Auditor course now!
Who implements the Annex A Controls?
Majority of the Controls instituted in the ISO 27001 Annexure may be assumed to be under the jurisdiction of the IT department. However, the standard thoroughly addresses all the three pillars of Information Security , namely people, processes and technology.
Moreover, the IT department does indeed contribute to the assessment and treatment of risk. Now most of the Controls demand the expertise of employees from all departments of the organisation, which entails the creation of a team comprising many departments. This newly made team will be responsible for handling the implementation process of the ISO 27001 Standard.
More importantly, it is generally the responsibility of the Information Security or Infosec Officer to lead the implementation process of the ISO 27001 Controls. They also oversee the organisation’s compliance with the standard’s guidelines and ISO 27001 Physical Security protocols. All the employees in the organisation are responsible for ensuring the integrity and application of the Controls instituted in the Annexure. Their responsibility owes to the reason that they are the organisation’s first line of defence against a threat or a cyber attack, hence being a shared responsibility
It is vital to note that the organisation’s management also needs to be onboard with the commitment to compliance of the standard as their review of the standard’s implementation is necessary. The review and approval of the ISO 27001 policies and processes also need to be handled by them.
Manage and improve your organisation’s ISMS by signing up for ISO 27001 Lead Implementer now!++
Is it necessary to adopt ISO 27001 in an organisation?
Here are a few provided benefits by ISO 27001 mentioned, from which your organisation can gain an advantage:
1) All forms of Information Security that includes cloud-based, paper-based, and digital data
2) Centrally managed framework provided to secure all types of information in one place
3) Quick response against security threats
4) High resilience to cyber-attacks
5) Cost mitigation to tackle ineffective defence technology
6) Protection of sensitive and confidential information to maintain the integrity
7) Protection against technology-based risks and other threats to ensure the complete safety of the organisation
Conclusion
This blog covers multiple areas of ISO 27001, comprising Controls, standards, benefits, and more. The ISO Standards can help businesses deal with risks and problems and convert them into opportunities. The ISO 270001 Controls protect your organisation and keep you focussed; to effectively achieve productivity and customer satisfaction and improve efficiency.
Upgrade your career in Information Security Management, by signing up for our ISO 27001 Certification now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 27001 Foundation
ISO 27001 Foundation
Mon 30th Sep 2024
Mon 21st Oct 2024
Mon 28th Oct 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024
Mon 16th Dec 2024
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


