We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +1 7204454674 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Ever thought about how companies keep their tech services ticking without a hitch, even when things get tough? It’s all thanks to smart management, especially ITIL Problem Management Roles and Responsibilities outlined in ITIL. This approach is all about digging deep to find, understand, and fix the underlying issues of hiccups so they don’t happen again. It’s like being a detective and a doctor for IT services, making sure problems are solved for good!
According to the report by PayScale, an average ITIL-certified professional earns an annual salary of about £42k. This blog breaks down of ITL Problem Management Roles and Responsibilties: the Process Owner, Analyst, Manager, and Coordinator. It’s like having a superhero team where each member has a special role in saving the day for IT services..
Table of Contents
1) What is ITIL Problem Management?
2) What are the steps of ITIL Problem Management?
3) Roles and responsibilities of ITIL Problem Management
4) Benefits of ITIL Problem Management
5) Conclusion
What is ITIL Problem Management?
ITIL Problem Management is like the guardian of IT services within the ITIL universe. It’s all about keeping a close eye on the entire life cycle of potential hiccups and making sure they’re nipped in the bud. The big goal? To stop problems in their tracks, lessen the headaches from any issues that do pop up, or better yet, keep them from happening at all.
This process is a mix of detective work and preventive care. It involves spotting, dissecting, and dealing with problems before they turn into bigger messes. By focusing on the main causes rather than just patching up the symptoms, ITIL Problem Management boosts the quality of services and cuts down on interruptions
What are the steps of ITIL Problem Management?
An ideal Problem Management process follows a certain set of steps, which allows it to identify and prioritise challenges in ITIL Project Management. These challenges are normally reported by users or the person operating the service desk as a countermeasure against potential errors in the future. Overall, this process can be divided into seven steps, which are as follows:
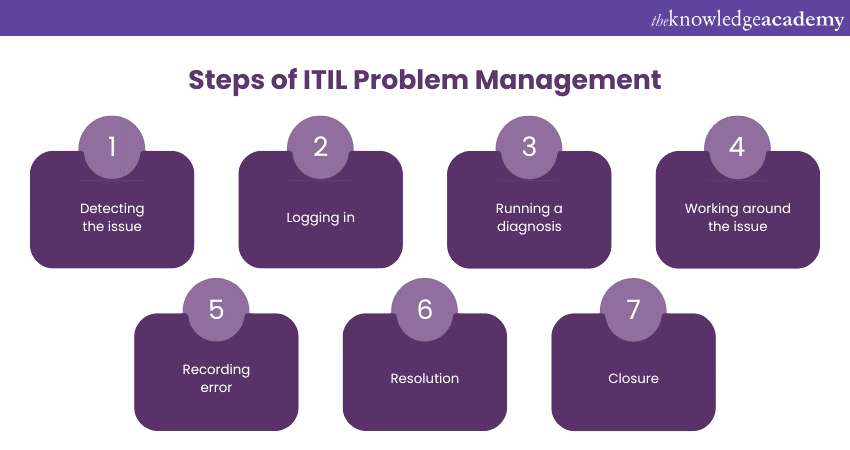
Step1: Detecting the issue
The first step is to acknowledge an issue to fix it, and this is no exception for the Problem Management process. Detecting a recurring issue allows you to investigate it further and analyse the root cause behind it. The most common example of a problem being identified by people is when an unexpected variation exists, that diverts the results from initial plan, however the cause of it is unknown.
Step 2: Logging in
Once a problem is detected, it is now reported to another team responsible for fixing it, a proper life cycle for the error starts. The details of the error or the problem is analysed, such as the date of occurrence and the severity of the said problem. This step also includes clearly analysing and classifying the problem under a specific category.
Step 3: Running a diagnosis
Once the problem and its type are determined, a diagnosis can be run. This includes accessing the database and trying to detect similar issues in the data body. The same issue occurring across the database on different occasions gauges any occurrence of a similar error.
Step 4: Working around the issue
A permanent solution promises that the problem will not come back, but a temporary work around lets you proceed back to work. Working around the said problem and navigating the hurdle is often considered the most effective counter measure rather than brute forcing your way through the problem and ceasing any productivity.
Step 5: Recording error
Once a problem is detected and diagnosed, it's time to record the error and maintain a history of similar issues. This helps you analyse if a problem is addressed, is being worked on, or is resolved. This serves the major function of removing any potential redundancy from the process of Problem Management.
Step 6: Resolution
Resolution is often considered an extension of record keeping, as they share some similarities. This process mostly focuses on the analysis of previous errors, which are resolved during the management process.
Not only does this process help you keep track of issues that have occurred in the past, but it also allows you to prepare for similar issues in the future. It simplifies the overall process of problem management, reducing the overall downtime due to errors.
Step 7: Closure
Closure is the last step of this process, to make sure every small segment and a larger body as whole is working as it was intended to. Closure commonly includes a permanent fix to a problem, thus removing the need to work on it in the future.
All those professionals interested in understanding the ITIL framework can join ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Training Course now!
Roles and responsibilities of ITIL Problem Management
As we delve into the intricate landscape of ITIL Problem Management Roles and Responsibilities, the ITIL guiding principles of remain instrumental in shaping the efficiency and success of these roles.
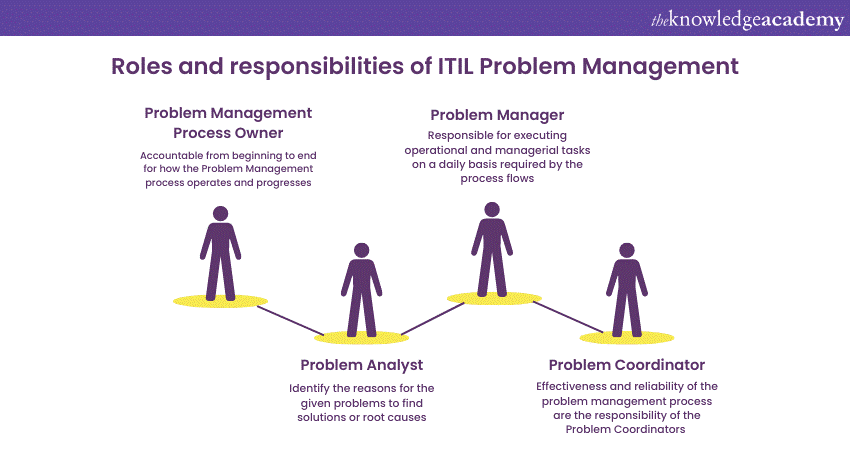
Problem Management Process Owner
The design and upkeep of the Problem Management process lifecycle have become the responsibility of the Problem Management Process Owner. Such an individual is accountable from beginning to end for how the Problem Management process operates and progresses.
Secondly, they are also responsible for the general well-being and accomplishment of the team's problem-solving process. The process and all supporting documents belong to the Problem Management process owner. The Process Owner and Managers will focus on continuously improving the Problem Management process.
Problem Analyst
The role of a Problem Analyst is to identify the reasons for the problems to find solutions or root causes by enquiring and taking the help of necessary subject matter experts. Further, the information about the resolution of occurrences is documented. Secondly, they are also responsible for examining and deciding whether to accept or reject given errors for a particular problem. Thirdly, they are responsible for implementing remedial measures and fixing known errors.
The number of problems and the time it takes to resolve them have reduced over time thanks to the utilisation of this data to accelerate resolution and pinpoint long-lasting remedies. Business-critical systems have less downtime and interruption as a result.
Problem Manager
Playing a central role in the Problem Management process, there is a Problem Manager who operates within the ITIL framework to minimise disruptions in IT service. Problems are to be identified by analysing incident records, Incident Management trends, and IT operation teams' feedback
In case they are identified, logging and categorisation of the problems systematically are mandatory so as to handle them efficiently. It may include ensuring that each of the problems is duly documented with all the relevant details, classified according to the nature and impact of the same, and further prioritised in accordance with its potential effect on the business operation.
Thereafter, the Problem Manager will manage the problem throughout its life cycle up to resolution, which will include arrangements for full root-cause investigation and diagnosis, workaround, or permanent solution construction and implementation. He also ensures that the problem is rectified and preventive changes are implemented to reduce the chances of the problem reoccurring, working in coordination with the other IT service management processes and executives responsible.
Problem Coordinator
A problem Coordinator, typically a service owner, guides a problem through the Problem Management process. The Problem Coordinator must have the appropriate functional role and is responsible for the Problem Management process's effectiveness and reliability. The Problem Coordinator also analyses from time to time to see whether any new issues need to be reported.
Problem Coordinators serve as the watchdogs for all known errors. They alert the Problem Manager, organise root cause analysis, and assign work and known errors to the Problem Analysts. They also ensure that the information entered and errors known in the problem investigations they manage are accurate and updated. Problem Coordinators take accountability for the problems they are responsible for and ensure that these problems progress through the problem management process in an appropriate and sequential path.
Know the key concepts of Direct, Plan and Improve and the role of Governance, Risk and Compliance by signing up for our ITIL® 4 Strategist: Direct, Plan And Improve DPI Training now!
Benefits of ITIL Problem Management
Problem Management can have a certain set of benefits when it is implemented successfully. Some of the advantages are mentioned below:
1) Constant Service Improvement (CSI): Proactively addressing issues with integrated ITSM operations results in enhanced service consistency and low downtime.
2) Mishap prevention: Proactive Problem Management saves significant costs by preventing detrimental incidents.
3) Productivity boost: Efficiency rises significantly when minor problems don't drain time and resources.
4) Agile resolutions: Using best practices in problem analysis lets you easily pinpoint and address service outages.
5) Root cause study: Problem Management lets you round up the previous records of errors, helping you avoid them in future.
6) Higher customer satisfaction: A consistent service promises better feedback from the customers, earning their loyalty.
7) Service restoration: Visible issues directly translates to increased speed at which a problem is addressed and fixed. As a result, you will witness quicker recovery.
8) Less interruptions: A holistic approach to problems results in more effective resolutions in the long run.
Conclusion
We hope this blog made you understand the various ITIL Problem Management Roles and Responsibilities. When these roles and responsibilities are clearly defined, they ensure accountability and efficiency throughout the process. By adopting these practices, organisations can mitigate the adverse effects of problems and foster a culture of continuous improvement and resilience against future challenges
Learn the ITIL framework and its role in ITSM by signing up for our ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The main goal of ITIL Problem Management is to eliminate recurring incidents and minimise the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented.

Defining roles and responsibilities within ITIL Problem Management ensures that every aspect of Problem Management is handled efficiently and effectively. This clarity promotes accountability and streamlines operations.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ITIL® Certification Training, including ITIL 4 Foundation Certification Course, ITIL 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support CDS, and ITIL 4 Specialist: Drive, Plan and Improve DPI. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ITIL 4 Guiding Principles.
Our IT Service Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to ITIL 4, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
Wed 18th Sep 2024
Mon 23rd Sep 2024
Mon 7th Oct 2024
Tue 15th Oct 2024
Sat 19th Oct 2024
Mon 21st Oct 2024
Mon 28th Oct 2024
Mon 4th Nov 2024
Tue 12th Nov 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Mon 2nd Dec 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024
Mon 16th Dec 2024
Thu 9th Jan 2025
Thu 13th Mar 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 11th Sep 2025
Thu 27th Nov 2025
Thu 18th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course.png)



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


